Sodium Ion Battery
Classification:
Products
Key words: Sodium Ion Battery
Product Description
Performance Advantages
Driven by global carbon neutrality goals, sodium-ion batteries have emerged as a prominent player in the energy storage sector due to their abundant resources, low cost, and exceptional safety. Sodium, with a crustal abundance of 2.75% (far exceeding lithium’s 0.0065%), is widely distributed globally, effectively mitigating risks associated with overdependence on lithium resources. Key advantages include a cost approximately half that of lithium-ion batteries, a cycle life of up to 3,000 cycles (compared to 300 cycles for lead-acid batteries), and stable operation in extreme temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C, making them ideal for energy storage in frigid regions and winter electric vehicle charging. Additionally, sodium-ion batteries utilize aluminum foil for both cathode and anode current collectors, further reducing material costs. Haosheng New Energy’s achievements include collaborative innovation with Southwest University through a joint sodium-ion battery materials laboratory, extensive industry validation via sample testing with leading companies like Vision Technology, Lishen New Energy, and Guoxuan High-Tech, three generations of technological breakthroughs in cathode materials (with the latest polyanionic system achieving advanced performance), and accelerated industrialization with an annual production capacity of 20,000 tons of sodium-ion battery materials across a 183-acre facility.
Product Specifications
1. Composite Sodium Iron Phosphate (NFPP)
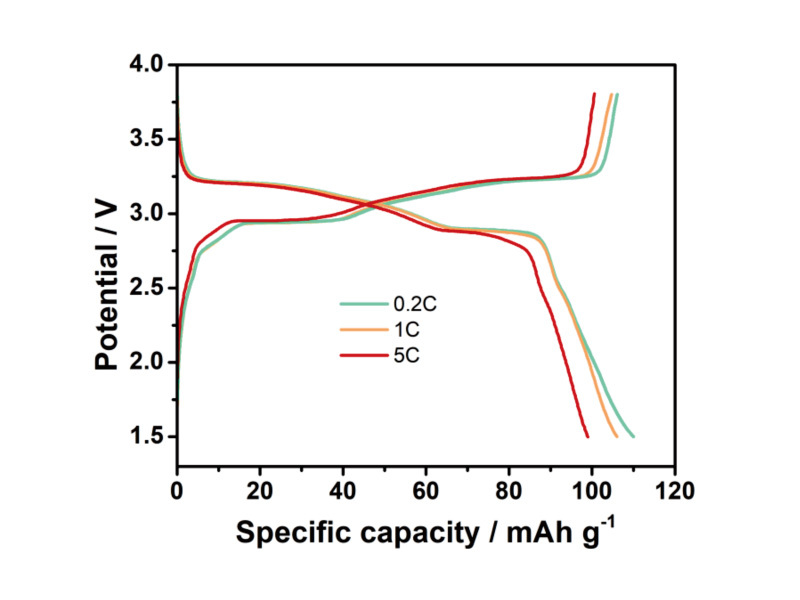
a. High Specific Capacity: 110 mAh/g (industry-leading).
b. Long Cycle Stability: 80% capacity retention after 3,000 cycles (half-cell).
c. High Rate Performance: 90% capacity retention at 5C.
d. Low pH Value: pH 9.3, ensuring excellent processability.
e. Cost Advantage: Strict cost control for significant cell-level competitiveness.
2. Sodium-Compensated NFPP (S-NFPP)
a. Exclusive Sodium-Supplement Coating: Enhances initial charge capacity without compromising electrochemical or processing performance.
b. Energy Density: Enables full-cell initial Coulombic efficiency exceeding 95%.
c. Cycle Performance: Forms a sodium slow-release layer on the anode to improve cycling stability.
d. pH Reduction: Further lowers material pH to 9.3.
e. Cost Advantage: Maintains cell-level cost leadership.
3. Sodium Compensation Agent (NaCrO₂)
a. High Sodium Content: Maximizes active material utilization for enhanced energy storage.
b. Gas-Free Design: Ensures structural stability and safety.
c. Broad Compatibility: Delivers performance improvements across diverse sodium battery systems.
Previous Page
Next Page
Related Products
Product Consulting